What Do IVF Injections Really Do to Your Body
If you’re preparing for in vitro fertilization (IVF), you’ve probably heard a lot about the daily injections that form a big part of the treatment. For many patients, this is one of the most intimidating steps. The good news is that IVF injections are carefully designed to help your body produce multiple healthy eggs, prepare your uterus for embryo transfer, and give your treatment the best possible chance of success.
In this article, we’ll explain what IVF injections are, how they work, and what you can expect during the process. By the end, you’ll understand why these fertility shots are so crucial to the IVF journey.
What Are IVF Injections?
IVF injections are a series of hormone-based medications given by injection throughout an IVF cycle. They are sometimes called fertility shots, and they serve several different purposes, from stimulating the ovaries to preventing premature ovulation. Unlike typical monthly cycles, where one egg matures, these medications allow doctors to collect multiple eggs, increasing the chances of fertilization and embryo development.
Why IVF Injections Are Necessary

The goal of IVF is to maximize the number of eggs available for fertilization in a single cycle. Injections help achieve this by:
● Stimulating the ovaries to produce multiple eggs.
● Controlling timing so eggs don’t release too early.
● Preparing the uterine lining for implantation.
● Supporting early pregnancy with hormones after embryo transfer.
Without these medications, doctors would only be able to retrieve one egg per cycle, drastically lowering the chances of success.
Types of IVF Injections and Their Functions
IVF injections aren’t all the same. Each medication has a unique purpose, and together they work in harmony to optimize the chances of conception. Here’s a closer look:
1. Ovarian Stimulation Injections
This is the first major stage of IVF injections. These shots use hormones like follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) to encourage your ovaries to mature more than one egg. In a natural cycle, only one egg usually matures, but IVF requires multiple eggs to maximize the chances of creating viable embryos.
● How they work: FSH stimulates the follicles in the ovaries to grow, while LH helps support egg development.
● Examples: Gonal-F, Follistim, Menopur.
● Duration: Typically administered daily for 8–14 days.
● What to expect: You’ll attend regular monitoring appointments, including ultrasounds and blood tests, to track follicle growth and hormone levels.
These injections are crucial because the number and quality of eggs retrieved directly influence the success of the IVF cycle.
2. Antagonist or Agonist Injections
As your ovaries respond to stimulation, there’s a risk that eggs could release too soon, which would disrupt the entire cycle. To prevent this, doctors prescribe GnRH antagonists or agonists.
● GnRH antagonists (e.g., Cetrotide, Ganirelix): These medications act quickly to block the natural surge of luteinizing hormone (LH), which triggers ovulation.
● GnRH agonists (e.g., Lupron): These work differently by overstimulating and then suppressing natural hormone signals, giving doctors more control over timing.
● Purpose: Keep eggs safely in the ovaries until the scheduled egg retrieval.
● Timing: Usually introduced around the middle of the stimulation phase.
These injections essentially act like a “pause button,” ensuring that ovulation happens only when your doctor is ready.
3. The Trigger Shot
Once monitoring shows that your eggs have matured, it’s time for the trigger shot. This injection is a critical turning point in the IVF process.
● What it is: A dose of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) or, in some cases, a GnRH agonist.
● What it does: Mimics the natural hormonal surge that completes egg maturation and prepares them for retrieval.
● Timing: Given about 34–36 hours before egg retrieval.
The timing of this shot is essential — too early, and the eggs may be immature; too late, and you risk missing the retrieval window. This precision is why monitoring and communication with your clinic are so important.
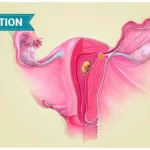
4. Progesterone Support Injections
After embryo transfer, your body needs extra support to create the right environment for implantation. That’s where progesterone injections come in.
● What they do: Help thicken and stabilize the uterine lining, making it more receptive to the embryo.
● Duration: Usually started after egg retrieval and continued for several weeks into early pregnancy.
● Forms: Progesterone can be given by injection, vaginal suppository, or gel, depending on your clinic’s protocol.
Without this hormone support, the chances of successful implantation may decrease. Progesterone injections are often the final stage of the IVF injection process.
The IVF Injections Timeline
The exact schedule depends on your personalized treatment plan, but here’s what a typical cycle looks like:
- Stimulation phase (Day 1–14): Daily FSH/LH injections to grow multiple eggs.
- Mid-cycle (Day 5–12): Antagonist or agonist injections added to prevent premature ovulation.
- Trigger shot (Day 12–14): One injection to mature eggs right before retrieval.
- Post-transfer (after Day 15): Progesterone injections or supplements to support implantation and early pregnancy.
From start to finish, you may give yourself one to two injections per day for several weeks, depending on your doctor’s protocol.
What to Expect During IVF Injections
Physical Effects
● Mild bloating and abdominal discomfort.
● Tenderness at the injection site.
● Mood changes due to hormone fluctuations.
● Occasional headaches or fatigue.
These side effects are common but usually manageable. Your care team will monitor you closely with blood tests and ultrasounds to ensure your body is responding appropriately.
Emotional Experience
For many patients, the thought of daily injections feels overwhelming. It can help to remember that these shots are temporary and a critical step toward your ultimate goal. Many clinics also provide training on how to administer them safely and comfortably.
Tips for Managing IVF Injections

● Stay organized: Use a calendar or app to track each dose.
● Rotate injection sites: This prevents bruising and soreness.
● Use ice or numbing cream: Helps reduce discomfort.
● Take it step by step: Don’t focus on the entire cycle; just manage each day.
● Lean on support: Partners, friends, or support groups can make the process less stressful.
Emotional Impact of IVF Injections
It’s not just about the physical shots — IVF injections can also take an emotional toll. Many patients report feeling anxious, stressed, or even guilty if they struggle with the process. It’s important to remember:
● These feelings are normal.
● Seeking support from counsellors or therapy can be helpful.
● Sharing your experience with others on the same journey can reduce the sense of isolation.
Summary: Why IVF Injections Matter
So, what do IVF injections do? Simply put, they give your body the best chance to produce multiple healthy eggs, prevent premature release, and prepare your uterus for pregnancy. While they may seem intimidating, these injections are a vital step in the IVF process. With careful monitoring, proper guidance, and emotional support, most patients find them manageable. If you’re beginning your IVF journey and want expert care at every step — from injections to embryo transfer — book a consultation with The Bridge Clinic’s IVF specialists today. With advanced treatments and compassionate support, we’ll guide you toward turning your dream of parenthood into reality.
Follow us on our social media channels below:
Explore our related articles below: